Tricuspid Regurgitation - Severe Auscultation Lesson with Recordings
Virtual Auscultation
The patient's position is supine.
Lesson
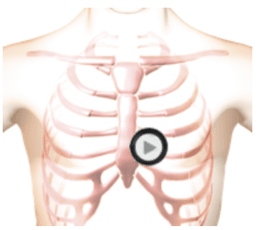
This is an example of severe tricuspid regurgitation which is caused by degeneration of the tricuspid valve leaflets. The first heart sound is normal. The second heart sound is unsplit. There is a loud, rectangular, pansystolic murmur. There is a brief, rumbling, diamond-shaped diastolic murmur. In the anatomy video you can see the enlarged right atrium and right ventricle. You can see the turbulent blood flow from the right ventricle into the right atrium. This is the systolic murmur. You can see the brief turbulent blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle in diastole. This is caused by too much blood in the right atrium which forces blood back into the ventricle during diastole producing the flow rumble. To differentiate tricuspid regurgitation from mitral regurgitation, the maximum intensity of the tricuspid murmur is heard at the left lower sternal border. In addition, the murmur intensity increases with inspiration.Waveform
Heart Sounds Video
Review the animation. Observe the enlarged right atrium and right ventricle.
You can see the turbulent blood flow from the right ventricle into the right atrium. This is the systolic murmur.
Notice the brief turbulent blood flow from the right atrium to the right ventricle in diastole. This is caused by too much blood in the right atrium which forces blood back into the ventricle during diastole producing the flow rumble.
To differentiate tricuspid regurgitation from mitral regurgitation, the maximum intensity of the tricuspid murmur is heard at the left lower sternal border. In addition, the murmur intensity increases with inspiration.
Authors and Sources
Authors and Reviewers
-
Heart sounds by Dr. Jonathan Keroes, MD and David Lieberman, Developer, Virtual Cardiac Patient.
- Lung sounds by Diane Wrigley, PA
- Respiratory cases: William French
-
David Lieberman, Audio Engineering
-
Heart sounds mentorship by W. Proctor Harvey, MD
- Special thanks for the medical mentorship of Dr. Raymond Murphy
- Reviewed by Dr. Barbara Erickson, PhD, RN, CCRN.
-
Last Update: 12/11/2022
Sources
-
Heart and Lung Sounds Reference Library
Diane S. Wrigley
Publisher: PESI -
Impact Patient Care: Key Physical Assessment Strategies and the Underlying Pathophysiology
Diane S Wrigley & Rosale Lobo - Practical Clinical Skills: Lung Sounds
- Essential Lung Sounds
Diane S. Wrigley, PA-C
Published by MedEdu LLC - PESI Faculty - Diane S Wrigley
-
Case Profiles in Respiratory Care 3rd Ed, 2019
William A.French
Published by Delmar Cengage - Essential Lung Sounds
by William A. French
Published by Cengage Learning, 2011 - Understanding Lung Sounds
Steven Lehrer, MD
- Clinical Heart Disease
W Proctor Harvey, MD
Clinical Heart Disease
Laennec Publishing; 1st edition (January 1, 2009)